RECOMMENDED USES: This safety footwear is indicated for the following uses:
With perforation resistant insert: civil and road construction, engineering, demolition, work in storage areas and warehouses, in stone quarriers, mines, junkyards, and work in the open air.
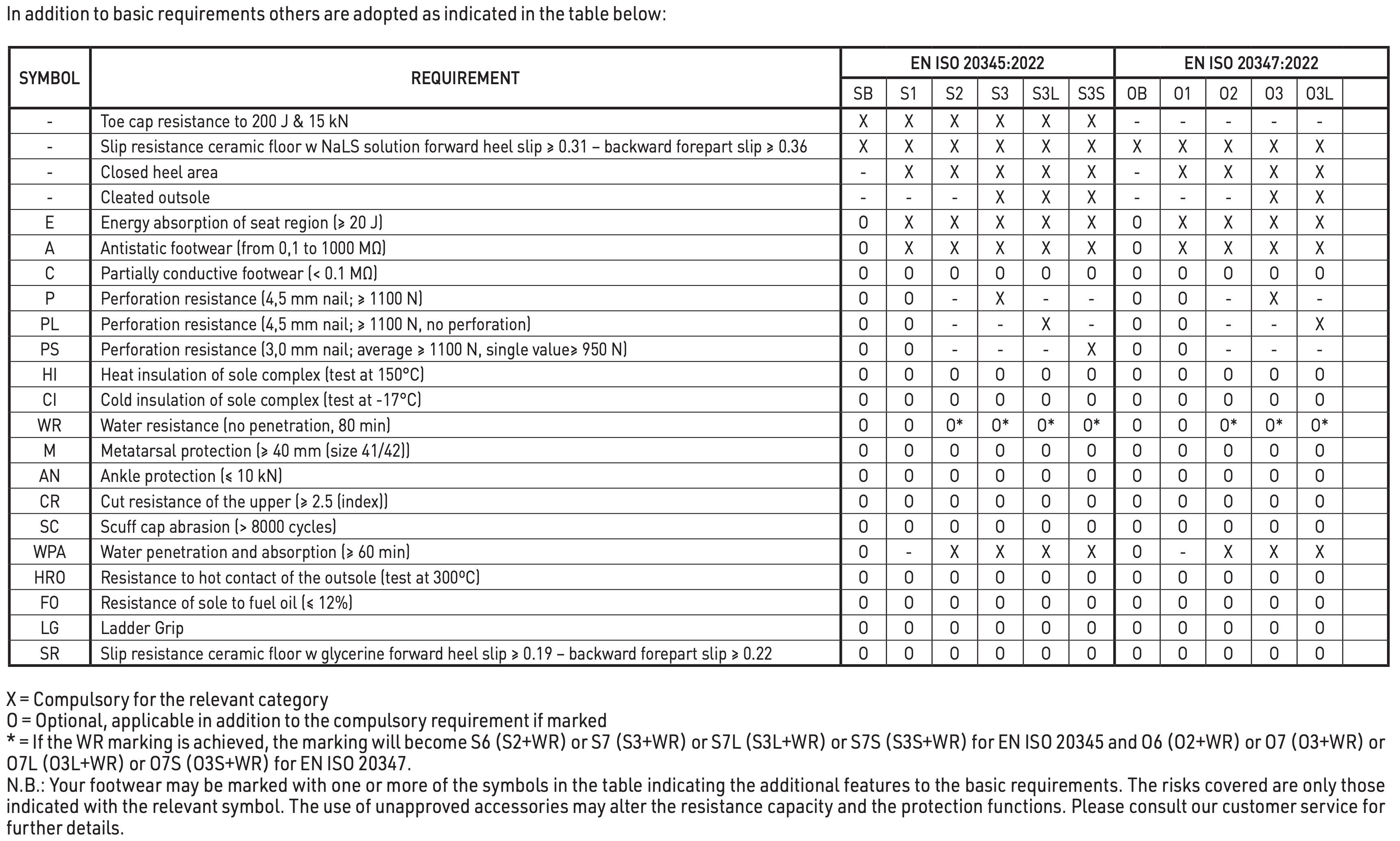
The perforation resistance of this footwear has been measured in the laboratory using standardized nails and forces. Nails of smaller diameter and higher static or dynamic loads will increase the risk of perforation occurring. In such circumstances alternative preventative measures should be considered.
Three generic types of perforation resistant inserts are currently available in PPE footwear. These are metal types and those from non-metal materials, which shall be chosen on basis of a job-related risk assessment. All types give protection against perforation risks, but each has different additional advantages or disadvantages including the following:
Metal (P): is less affected by the shape of the sharp object/hazard (e.g. diameter, geometry, sharpness) but due to shoemaking limitations does not cover the entire lower area of the shoe.
Non-metal (PL or PS): may be lighter, more flexible and provide greater coverage area when compared with metal but the perforation resistance may vary more depending on the shape of the sharp object/hazard (e.g. diameter, geometry, sharpness). Two types in term of the protection afforded are available. Type PS may offer more appropriate protection from smaller diameter objects than type PL.
“Metal perforation resistant insert” or “Non-Metal perforation resistant insert” on the box label indicates the type of insert used.
For more information about the type of perforation resistant insert provided in your footwear please contact the manufacturer or supplier detailed on these instructions.
Without perforation resistant insert: work on bridges and elevated structures, in elevators, blast furnaces, large pipelines, cranes, boilers and burners, installation of heating and air-conditioning systems, transformation and maintenance activities, metallurgical or similar works, the production and working of flat glass, the handling of moulds and dies in the ceramics industry, work in the construction materials, handling and storage industry, the handling of blocks of frozen meat and metal ship containers, railway freight
yards;
With quick unlacing: in case of interventions where the footwear must be removed quickly;
With protective scuffcap: in the case of prolonged and/or repeated friction of the toe-tip against the ground;
LIMITATIONS OF USE: The footwear is not suitable for protection against risks not referred to in this information leaflet and in particular those covered by third-category personal protection equipment as defined in Regulation (EU) 2016/425.
USE AND MAINTENANCE: The manufacturer declines all responsibilities for any damage and consequences resulting from improper use of the footwear. When choosing the footwear, it is important to select a model and size suitable for your specific protection requirements. The footwear maintains the safety characteristics indicated only if worn and fastened correctly. The protection against risks indicated on the marking only applies to footwear in a good state of preservation. Before each use, carefully check the perfect state of preservation of the equipment and change it if you notice signs of alteration (excessive wear of the sole, stitching in poor condition, sole coming away from the upper, etc.). Footwear with a fast removal device: ensure that the rod of the device is properly inserted; the footwear is removed by gripping the end of the rod and pulling towards you. The characteristics of the footwear are best maintained when it is kept in good condition and it should therefore be cleaned regularly with brushes, cloths, etc., removing any stains with a damp cloth. Depending on the conditions of the workplace, the leather upper should be treated from time to time with normal polish or grease for shoes. Do not dry the footwear close to or in direct contact with sources of heat, such as heaters, radiators, etc. Do not use aggressive products such as benzene, acids and solvents, as they could have a negative effect on the quality, safety and lifetime of the PPE. Do not leave exposed to direct sunlight nor to high or low temperatures. Never tamper with the shoe in any of its parts.
PRESERVATION AND DISPOSAL: In view of the many different environmental factors involved, such as humidity and heat, it is not possible to define a definite shelf life.
Generally speaking, footwear with Polyurethane bottoms has a presumable shelf life of three years, provided it is kept in a dry and ventilated storage place where the temperature is not too high. Dispose of the device in compliance with current standards on environment safeguard and differentiated waste collection. This footwear is produced without using toxic or harmful materials. It is classified as non-hazardous waste and is certified with the European Waste Code (EWC):
Leather: 04.01.99 / Fabric: 04.02.99 / Cellulose material: 03.03.99
Metal materials: 17.04.99 or 17.04.07
Supports lined with PU and PVC, elastomeric and polymeric material: 07.02.99 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
ANTISTATIC FOOTWEAR: Antistatic footwear should be used if it is necessary to minimize electrostatic build-up by dissipating electrostatic charges, thus avoiding the risk of spark ignition of, for example, flammable substances and vapours, and if the risk of electric shock from mains voltage equipment cannot be completely eliminated from the workplace. Antistatic footwear introduces a resistance between the foot and ground but may not offer complete protection. Antistatic footwear is not suitable for work on live electrical installations.
It should be noted, however, that antistatic footwear cannot guarantee adequate protection against electric shock from a static discharge as it only introduces a resistance between foot and floor. If the risk of static discharge electric shock, has not been completely eliminated, additional measures to avoid this risk are essential. Such measures, as well as the additional tests mentioned below, should be a routine part of the accident prevention programme at the workplace.
Antistatic footwear will not provide protection against electric shock from AC or DC voltages. If the risk of being exposed to any AC or DC voltage exists, then electrical insulating footwear shall be used to protect from against serious injury.
The electrical resistance of antistatic footwear can be changed significantly by flexing, contamination or moisture. This footwear might not perform its intended function if worn in wet conditions.
Class I footwear can absorb moisture and can become conductive if worn for prolonged periods in moist and wet conditions. Class II footwear is resistant to moist and wet conditions and should be used is if the risk of exposure exists.
If the footwear is worn in conditions where the soling material becomes contaminated, wearers should always check the antistatic properties of the footwear before entering a hazard area.
Where antistatic footwear is in use, the resistance of the flooring should be such that it does not invalidate the protection provided by the footwear.” It is recommended to use antistatic socks.
“It is, therefore, necessary to ensure, that the combination of the footwear its wearers and their environment is capable, to fulfil the designed function of dissipating electrostatic charges, and of giving some protection during its entire life. Thus, it is recommended, that the user establish an in-house test for electrical resistance, which is carried out at regular and frequent intervals.
PARTIALLY CONDUCTIVE FOOTWEAR: Electrically partially conductive footwear should be used if it is necessary to minimize electrostatic charges in the shortest possible time, e.g. when handling explosives. Electrically partially conductive footwear should not be used, if the risk of shock from any electrical apparatus or live parts with AC or DC voltages has not been completely eliminated. In order to ensure that this footwear is partially conductive, it has been specified to have an upper limit of resistance of 100 kΩ in its new state.
During service, the electrical resistance of footwear made from conducting material can change significantly due to flexing and contamination, and it is necessary to ensure, that the product is capable of fulfilling its designed function of dissipating electrostatic charges during its entire life. Where necessary, it is therefore recommended, that the user establish an in-house test for electrical resistance and use it at regular intervals. This test and those mentioned below should be a routine part of the accident prevention program at the workplace.
If the footwear is worn in conditions where the soling material becomes contaminated with substances that can increase the electrical resistance of the footwear, wearers should always check the electrical properties of their footwear before entering a hazard area.
It is recommended to use an electrical dissipative socks.
Where partially conductive footwear is in use, the resistance of the flooring should be such that it does not invalidate the protection provided by the footwear. In use, no insulating elements should be introduced between the inner sole of the footwear and the foot of the wearer. If an insert (i.e. insocks, socks) is put between the inner sole and the foot the combination footwear/insert should be checked for its electrical properties.
REMOVABLE INSOCK: If the safety footwear is equipped with a removable insock this means that the tests were carried out with the insock in place. Always use the footwear with its insock in place! Replace the insock only with an equivalent model from the same original footwear supplier or from an insole supplier, which will supply insocks that fulfil the properties of this standard in combination with the expected safety footwear.
If the footwear is supplied without an insock this means that the tests were carried out without them.ear only insocks that fulfill the properties of this standard in combination with the identified safety footwear.
Some of our footwear models are suitable for use with SECOSOL orthopaedic insocks.
For further information, please see our website www.sixton.it
CRITERIA FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF THE STATE OF FOOTWEAR: Safety footwear should be replaced when any of the signs of wear identified below are found. Some of these
criteria can vary according to the type of footwear and materials used:
• Beginning of pronounced and deep cracking affecting half of the upper material thickness (Figure a);
• Strong abrasion of the upper material, especially if the toe puff or the toecap is revealed (Figure b)
• The upper shows areas with deformations or split seams in the leg (Figure c)
• The outsole shows cracks higher than 10 mm long and 3 mm deep (Figure d);
• Cleat height for cleated outsoles at any point lower than 1,5 mm (Figure e);
• Destruction of the lining or sharp borders of the toe protection which could cause wounds (Figure f)
• Upper/outsole separation of more than 15 mm long and 5 mm deep (Figure g);
• Delamination of the soling materials (Figure h);
• Pronounced deformation of the outsole due to heat exposure any of the following causes (Figure i):
- joining of 2 or more cleats due to the material melting;
- decrease of the height of any cleat to less than 1,5 mm;
- melting of the outside of the cleat and the midsole becomes visible;
• Original insock/s (if any) showing pronounced deformation and crushing;
• The closing mechanism is not in working order (zip, laces, eyelets, touch and dose system).